India’s Gross Domestic Product (GDP) has become a central focus of global economic discussions over the past few years. As the world’s most populous country and the fifth-largest economy, India continues to demonstrate remarkable economic resilience and potential. With a dynamic mix of traditional industries, cutting-edge technology, and a rapidly growing middle class, the Indian economy presents a fascinating case study in sustained economic development.
What is GDP and Why It Matters
Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is the total market value of all goods and services produced within a country in a specific period. It is a key indicator used to gauge the health of a nation’s economy. For India, GDP reflects not only economic growth but also the impact of government policies, global market trends, and internal structural reforms.
India’s GDP Growth: Recent Trends
As of mid-2025, India is expected to achieve a real GDP growth rate of around 6.7%, making it one of the fastest-growing major economies in the world. Here are some key developments:
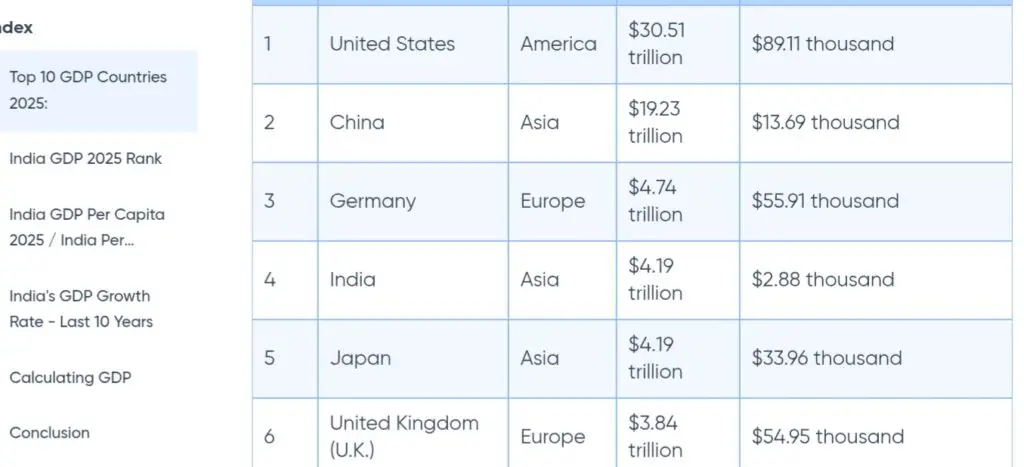
FY 2024-25 GDP size: Estimated at usd6.9lakh crore (approx. $3.7 trillion).
Nominal GDP growth (including inflation): 10.5%, higher than many developed economies.
Per capita GDP (2025 estimate): Around $2,700 USD, reflecting improved living standards but still behind countries like China and Brazil.
This growth is driven by strong domestic demand, recovery in services, a boom in digital and manufacturing sectors, and major government investments in infrastructure.
Key Sectors Driving India’s G
1. Services Sector (53% of GDP)India’s services sector—especially IT, finance, telecommunications, tourism, and e-commerce—continues to be a strong contributor to the economy. The global demand for Indian software services, BPOs, and fintech innovations remains robust.
2. Industry & Manufacturing (25% of GDP)Boosted by the “Make in India” and “Production Linked Incentive (PLI)” schemes, sectors like electronics, pharmaceuticals, auto manufacturing, and renewable energy have seen notable growth.
3. Agriculture (18% of GDP)While agriculture’s share in GDP has declined over time, it still provides livelihood to nearly 40% of India’s workforce. Government subsidies, agri-tech startups, and monsoon patterns play a key role here.
4. Construction & Real Estate -Urbanization, smart city projects, and increased foreign investments in real estate have revitalized this sector. Affordable housing schemes also stimulate demand.
Factors Fueling GDP Growth–
Demographic Dividend: Over 65% of India’s population is under 35, providing a massive labor and consumer base.
Digital Economy: UPI, digital banking, and widespread internet access have accelerated financial inclusion and business growth.
Reforms and Policies: GST, Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code (IBC), ease of doing business, and FDI liberalization attract investors.
Infrastructure Investments: High-speed rail, expressways, metro rail projects, and renewable energy parks create both jobs and economic output.
Infrastructure Investments: High-speed rail, expressways, metro rail projects, and renewable energy parks create both jobs and economic output.
Start-up and Innovation Ecosystem: India is home to over 100 unicorns, with a vibrant culture of entrepreneurship supported by incubators and VC funding.
Challenges Ahead
Despite its upward trajectory, India’s GDP faces several internal and external challenges:
Unemployment: Job creation hasn’t always kept pace with economic growth, especially among educated youth.
Income Inequality: Wealth distribution remains uneven, affecting social cohesion and long-term sustainability.
Global Uncertainty: Geopolitical tensions, commodity price volatility, and inflation can dampen growth.
Climate Change & Agriculture Dependence: Unpredictable weather affects crop yields and rural incomes.
Public Debt: India’s fiscal deficit and rising public debt need prudent management.
Future Outlook: Toward a $5 Trillion Economy.
India’s goal of becoming a $5 trillion economy by 2027 is ambitious but not unrealistic. It will require.
Continued reforms in labor laws, land acquisition, and taxation.
Stronger public-private partnerships in infrastructure and innovation.
A greater focus on education, health, and skill development to improve productivity.
Improved ease of doing business and contract enforcement.
Expansion of trade and manufacturing exports.
Conclusion.
India’s GDP growth story is one of resilience, innovation, and aspiration. With the right policy mix and inclusive growth strategies, India is well-poised to not only maintain its position as a global economic powerhouse but also improve the quality of life for its 1.4 billion citizens. The coming decade holds great promise, and India’s economic journey will be one of the most closely watched narratives in the global arena.
.
