Introduction
Natural gas is a cornerstone of global energy systems. Clean-burning, efficient, and versatile, it powers industries, heats homes, and increasingly supports electricity generation. As nations push for cleaner energy transitions while securing their energy independence, natural gas plays a pivotal role. With the world’s demand for energy rising, knowing who holds the keys to the largest reserves of this critical resource is vital.
In this article, we dive deep into the Energy Ranked list of countries with the largest proven natural gas reserves, explore the geopolitical implications, and look at how these nations are leveraging their energy wealth on the global stage.
Top 10 Countries by Proven Natural Gas Reserves (2025 Estimates)
Based on the latest available data (from BP Statistical Review, OPEC, and national sources), here are the countries with the largest proven natural gas reserves in trillion cubic meters (tcm):

1. Russia – 37.4 tcm
Russia holds the largest proven natural gas reserves in the world. Its massive deposits are located primarily in Siberia and the Arctic region, including the Yamal Peninsula and Western Siberia.
Key Gas Fields: Yamal, Urengoy, and Shtokman.
Export Power: Russia exports natural gas via pipelines (Nord Stream, TurkStream) and increasingly through LNG (Liquefied Natural Gas).
Geopolitical Role: Russia’s energy exports are a strategic tool, especially in Europe and Asia.
2. Iran – 32.1 tcm
Iran has the second-largest reserves, primarily in the South Pars/North Dome field, which it shares with Qatar.
Key Gas Fields: South Pars, Kish, and North Pars.
Challenges: Sanctions limit Iran’s ability to fully monetize its gas reserves.
Potential: Huge untapped potential if geopolitical tensions ease.
3. Qatar – 24.7
Qatar, despite its small size, is a global gas powerhouse, thanks to its share in the North Dome gas field, the world’s largest.
Global Influence: Top LNG exporter.
Infrastructure: Highly developed LNG terminals and shipping fleet.
Alliances: Strong energy ties with Asia—especially China, Japan, and South Korea.
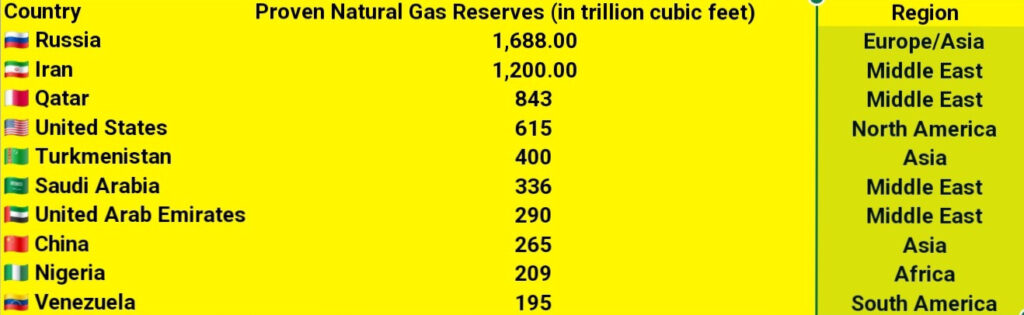
4. Turkmenistan – 19.5 tcm
Turkmenistan’s reserves lie in the Galkynysh field, one of the world’s largest.
Underdeveloped: Poor infrastructure limits full-scale exports.
Strategic Location: Sits near major Asian markets.
China Link: Major gas supplier to China through the Central Asia-China gas pipeline.
5. United States – 14.8
The U.S. is both a natural gas superpower and a major LNG exporter.
Shale Revolution: Hydraulic fracturing has unlocked vast reserves.
Top Producer: World’s largest natural gas producer (not just in reserves)
Export Growth: Rapid expansion of LNG terminals along the Gulf Coast.
6. China – 8.9 tcm

China has large reserves but also enormous domestic demand.
Energy Security: Investing heavily in gas exploration and production.
Imports: Major importer of LNG and pipeline gas.
Green Transition: Replacing coal with gas to reduce emissions.
Green Transition: Replacing coal with gas to reduce emissions.
7. Venezuela – 6.3 tcm
Venezuela has large reserves but underutilized potential due to economic and political instability.
Key Fields: Offshore and Orinoco Belt.
Challenges: Infrastructure collapse and sanctions.
8. Saudi Arabia – 6.0 tcm
While known for oil, Saudi Arabia also has significant gas reserves.
Vision 2030: Plans to shift electricity generation from oil to natural gas.
Investment: Expanding domestic gas production to support its industrial base.
9. United Arab Emirates – 5.8 tcm
The UAE is rapidly scaling its gas sector to reduce reliance on imports and diversify energy use.
New Discoveries: Major recent gas finds in Jebel Ali and offshore Abu Dhabi
LNG Exports: Developing export capacity
10. Nigeria – 5.5 tcm
Africa’s leader in gas reserves.
Gas Flaring: Still flares a significant amount of gas due to poor infrastructure.
LNG Potential: Nigeria LNG is one of the largest LNG exporters in Africa.
Investment Drive: Attracting foreign investment to boost gas production.
Honorable Mentions
Algeria – North Africa’s energy hub, heavily exporting gas to Europe.
Australia – Significant offshore reserves, key player in Asia-Pacific LNG trade.
Canada – Large unconventional reserves, major North American gas supplier.
Global Implications of Gas Reserves
Energy Security
Countries with large gas reserves have strategic leverage. Nations in Europe and Asia rely on imports for energy stability, often placing them at the mercy of producer countries.
Geopolitics & Diplomacy
Control over gas supplies can be as influential as military power. Russia’s leverage over Europe and Qatar’s dominance in LNG markets underscore how natural gas shapes foreign policy.
Energy Transition
Natural gas is seen as a “bridge fuel”—cleaner than coal and oil, it supports the transition to renewables. Nations are using gas to lower emissions while maintaining energy reliability.
Challenges Ahead
Infrastructure Needs: Without pipelines, LNG terminals, or proper storage, reserves are just numbers.
Environmental Concerns: Methane leakage and reliance on fossil fuels remain issues.
Geopolitical Risks: Wars, sanctions, and political unrest can choke supply routes or limit access.
Conclusion
Natural gas will remain a cornerstone of the global energy mix for decades to come. Countries with vast reserves have a critical role to play in powering the world—and shaping its politics. As cleaner energy systems evolve, the importance of these reserves lies not just in quantity, but in how wisely they are developed, managed, and integrated into a sustainable global future.